Kratom has become increasingly well-known in recent years due to its distinct effects, which range from boosting energy at lower doses to providing sedative and pain-relieving benefits at higher doses.
Traditionally utilized in Southeast Asia for centuries, Kratom has been an essential part of folk medicine and daily life, helping laborers endure long hours of physical labor and individuals manage discomfort.
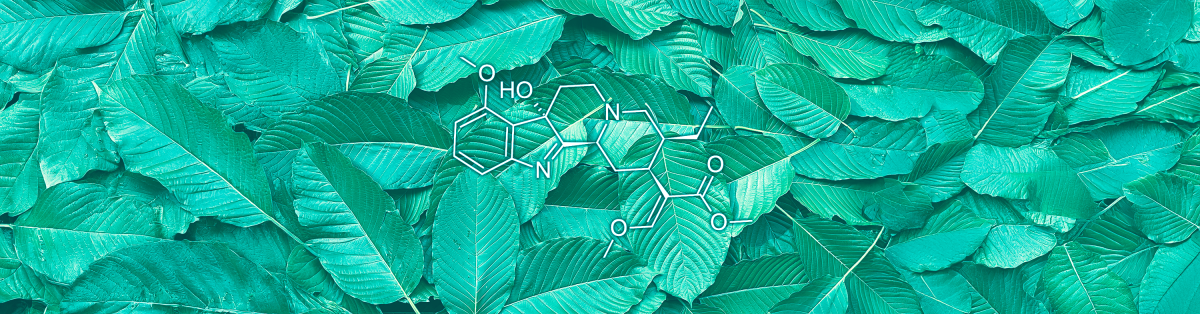
As modern research continues to examine its properties, one compound in particular has emerged for its remarkable potency—7-Hydroxy Mitragynine, also known as 7-OH.
But what exactly is 7-OH? What effects do 7-Hydroxy products produce, and how can users ensure its safe consumption? Let’s take a closer look at the role 7-Hydroxy plays in Kratom’s effects.

Understanding 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine
7-Hydroxy Mitragynine, or 7-OH, is a naturally occurring alkaloid found in Kratom (Mitragyna speciosa), a tropical tree native to Southeast Asia.
Among the more than 40 alkaloids identified in Kratom, 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is particularly noteworthy for its potent sedative and pain-relieving properties.
Although frequently mentioned alongside Mitragynine—the primary alkaloid in Kratom—7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is much stronger in its interaction with opioid receptors.
However, it exists only in trace amounts, accounting for less than 0.05% of the total alkaloid composition in Kratom leaves.
The Chemical Structure of 7-OH
7-Hydroxy belongs to the class of indole alkaloids, a category of naturally occurring compounds recognized for their complex molecular structures and biological effects.
It shares a structural similarity with Mitragynine but has one crucial difference: the addition of a hydroxyl (-OH) group at the seventh position in its molecular framework. This seemingly minor change significantly increases its potency and modifies how it interacts with the body’s opioid receptors.
This alkaloid’s structural properties enable it to bind more efficiently to the μ-opioid receptor, the primary receptor responsible for pain relief and euphoric sensations.
Research suggests that 7-Hydroxy is substantially stronger than Mitragynine in terms of receptor activity, with some findings indicating it could be up to 46 times more potent than Mitragynine and even several times stronger than morphine in certain lab-based studies.
However, because of its limited natural concentration, the majority of Kratom’s effects are attributed to Mitragynine, with 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine playing a lesser role.
Differences Between 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine and Mitragynine
Despite their structural similarities, the potency gap between Mitragynine and 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is considerable.
Mitragynine itself is a relatively weak opioid receptor agonist, meaning that while it interacts with opioid receptors, its effects are mild when compared to traditional opioids.
However, after ingestion, a portion of Mitragynine is metabolized into 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine, which exerts a much stronger effect on these receptors.
This metabolic conversion is one of the reasons Kratom’s effects can differ widely among individuals. Factors such as metabolic rate, liver enzyme function, and the particular Kratom strain consumed all play a role in determining how much 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is present in the body.
Additionally, certain drying and fermentation techniques used during Kratom processing may slightly elevate the natural levels of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine, though it remains a minor component relative to Mitragynine.
7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is an intriguing yet often misunderstood component of Kratom. While it is significantly more powerful than Mitragynine in its ability to engage opioid receptors, its naturally low concentration means its influence in traditional Kratom use is relatively minimal.
Most of Kratom’s effects stem from Mitragynine, with 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine playing a supporting role through metabolic conversion and natural oxidation.

How 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine Affects the Body
7-Hydroxy primarily exerts its effects by interacting with opioid receptors in the brain. As a potent agonist at the μ-opioid receptor (MOR), it plays a crucial role in Kratom’s sedative and analgesic properties.
Despite being present in only small amounts, this alkaloid has a much greater binding affinity than Mitragynine, making it a key factor in the plant’s pain-relieving effects.
Interaction with Opioid Receptors
The body has three primary opioid receptors: μ (mu), δ (delta), and κ (kappa).
Among them, the μ-opioid receptor is the most closely linked to pain relief, euphoria, and sedation.
Traditional opioids such as morphine, oxycodone, and heroin work by strongly activating this receptor, producing intense pain relief but also carrying a high risk of addiction and respiratory depression.
7-Hydroxy Mitragynine binds selectively to the μ-opioid receptor but behaves differently than conventional opioids. Although it has a high potency at these receptor sites, Kratom does not produce the same degree of respiratory suppression commonly linked to synthetic and semi-synthetic opioids.
This difference is thought to result from variations in receptor activation pathways.
Unlike full opioid agonists, which fully activate opioid receptor pathways and often cause severe side effects, 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine appears to act as a partial agonist with biased signaling.
This means it activates specific opioid receptor pathways more selectively, reducing the chances of respiratory depression while still offering strong pain relief.
Impact on Pain Perception and Mood
Because of its high opioid receptor affinity, 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine plays a significant role in Kratom’s analgesic effects. Many individuals seeking natural alternatives for managing chronic pain turn to Kratom for relief.
The alkaloid affects pain perception through central nervous system activity, diminishing discomfort while increasing tolerance to pain.
In addition to discomfort relief, 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine also affects mood. When the μ-opioid receptor is activated, dopamine is released in the brain’s reward system, creating sensations of relaxation and euphoria.
However, Kratom’s effects vary significantly with dosage. At lower doses, Mitragynine’s adrenergic properties promote stimulation, while at higher doses, the sedative effects of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine become more dominant.
Some users describe Kratom’s effects as providing a warm, contented, and relaxed feeling similar to opioids but without the cognitive impairment associated with prescription painkillers.
This makes it an attractive option for individuals looking for pain relief while maintaining mental clarity. However, excessive use may lead to tolerance and dependence, making moderation essential.
Metabolism and Conversion from Mitragynine
One of the most intriguing aspects of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is how it forms in the body. Unlike Mitragynine, which is abundant in Kratom leaves, 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is found in only trace amounts in raw plant material.
However, once Kratom is consumed, the liver metabolizes a portion of Mitragynine, converting it into 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine.
This metabolic process is critical to Kratom’s effects. Some individuals may experience more pronounced sedative or analgesic effects due to metabolic differences.
Factors such as genetic variations in liver enzymes, the presence of other substances in the system, and overall Kratom dosage influence how much 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is produced.
Because this conversion process is naturally limited, consuming raw Kratom does not typically result in dangerously high levels of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine.
However, when using concentrated products, such as 7-Hydroxy tablets, users must be cautious, as artificially high levels of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine can mimic the effects of opioids, increasing the potential risk of dependence.

The Potency and Effects of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine
7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is considered one of the most powerful alkaloids in Kratom, far more potent than its precursor, Mitragynine.
Its strong binding affinity to opioid receptors makes it a key player in Kratom’s sedative, pain-relieving, and mood-enhancing effects.
However, its high potency also raises concerns about tolerance, dependence, and potential misuse, especially when Kratom is taken in large amounts or when enhanced extracts are involved.
How Potent is 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine?
Studies have shown that 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is significantly stronger than Mitragynine in opioid receptor activity.
Research suggests that it could be up to 46 times more potent than Mitragynine and multiple times stronger than morphine in certain laboratory binding assays.
Despite its high receptor affinity, its natural presence in Kratom is quite low, typically comprising less than 0.05% of the total alkaloid content in dried leaves.
The potency of this alkaloid is a major factor in Kratom’s pain-relieving capabilities. While Mitragynine contributes to pain relief as a partial opioid receptor agonist, 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine has a significantly stronger effect on the μ-opioid receptor.
Even in small amounts, it enhances Kratom’s ability to ease discomfort, making it particularly appealing to individuals managing chronic pain, recovering from injuries, or seeking relief post-surgery.
This compound is also responsible for Kratom’s sedative properties, which become more pronounced at higher doses.
The shift from a stimulating effect at lower doses to a deeply relaxing effect at higher doses can be attributed to the increasing influence of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine as more of it accumulates in the body.
Effects of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine at Different Dosages
The effects of Kratom, particularly those influenced by 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine, are highly dose-dependent. At lower doses, Kratom tends to have stimulating and mood-boosting properties due to Mitragynine’s adrenergic activity.
However, as the dosage increases, the sedative and pain-relieving effects of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine become more pronounced.
Low Doses (1-3 grams of raw Kratom powder):
- Increased energy and alertness
- Mild euphoria and improved mood
- Enhanced focus and motivation
- Minimal pain relief
Moderate Doses (4-6 grams of raw Kratom powder):
- Heightened pain relief
- Moderate relaxation and reduced stress
- Mild to moderate sedation
- Decreased physical discomfort
High Doses (7+ grams of raw Kratom powder):
- Strong analgesia
- Deep sedation and relaxation
- Drowsiness and potential lethargy
- Increased risk of nausea and dizziness
While individual experiences vary due to metabolism, body weight, and tolerance, the presence of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine becomes increasingly significant as the dose rises.
The progression from mild stimulation to deep relaxation mirrors the effects of traditional opioids, which exhibit similar dose-dependent responses.
Tolerance, Dependence, and Withdrawal Considerations
Due to its strong activity at opioid receptors, frequent or excessive Kratom use can lead to tolerance and dependence over time.
Tolerance develops when the body adjusts to consistent opioid receptor activation, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effects. This occurs with most substances that interact with opioid receptors.
Dependence occurs when the body becomes reliant on Kratom’s alkaloids to maintain a sense of normalcy.
Regular users who consume Kratom daily, particularly in large amounts, may experience withdrawal symptoms if they suddenly stop taking it. Although Kratom withdrawal is generally milder than that of conventional opioids, it can include:
- Restlessness and irritability
- Muscle aches and joint discomfort
- Insomnia and sleep disturbances
- Fatigue and low energy
- Anxiety or mood fluctuations
While Kratom withdrawal is not typically life-threatening, the symptoms can make it difficult for habitual users to quit.
7-Hydroxy Mitragynine plays a significant role in withdrawal symptoms, as it engages opioid receptors similarly to traditional opioids, though with less intensity.
Potential Risks of High 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine Concentrations
Although naturally occurring Kratom contains only trace amounts of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine, concerns have been raised regarding extracts and enhanced products that artificially concentrate this alkaloid.
Because 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is significantly more potent than Mitragynine, elevated levels can lead to effects resembling those of prescription opioids, including an increased risk of dependence and respiratory depression.
Regulatory authorities in some countries have closely examined Kratom due to concerns that certain products might contain unnaturally high levels of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine.
These concerns stem from the possibility of synthetic enhancement or processing methods that artificially increase its concentration.
This has led to ongoing discussions about the safety and regulation of Kratom extracts and enhanced powders, particularly those that exceed natural alkaloid levels.
For users, consuming concentrated 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine requires extreme caution and precise dosing. A small amount can have powerful effects, so responsible consumption is essential.

How 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine Forms in Kratom
7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is one of the most potent alkaloids found in Kratom, yet its natural concentration in raw leaves is extremely low.
Unlike Mitragynine, which is the primary alkaloid in Kratom, 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is not produced in large amounts by the plant itself but instead forms through natural processes.
Understanding how this compound develops is essential to accurately assessing its role in Kratom’s effects and dispelling misconceptions about artificially enhanced products.
The Natural Conversion Process
Freshly harvested Kratom leaves mainly contain Mitragynine, with little to no detectable 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine.
Most of the 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine found in Kratom products results from the oxidation of Mitragynine, occurring either due to environmental exposure or through metabolic processes in the human body.
Several factors influence how much 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine forms in Kratom:
- Oxidation During Drying: When Kratom leaves are dried and exposed to oxygen, a portion of Mitragynine undergoes oxidation, forming 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine. The extent of this conversion depends on drying conditions, humidity, and light exposure. Sun-dried or fermented Kratom varieties tend to contain slightly higher levels of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine than fresh leaves.
- Fermentation and Aging: Certain post-harvest techniques, such as fermentation, enhance the conversion of Mitragynine into 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine. This explains why some aged or fermented Kratom strains, such as Bentuangie, have stronger sedative effects than unfermented varieties. The fermentation process modifies the alkaloid profile, increasing 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine levels slightly.
- Metabolic Transformation in the Body: When Kratom is ingested, the liver metabolizes Mitragynine, and a portion of it converts into 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine. This metabolic transformation is facilitated by liver enzymes, which are responsible for breaking down various substances. The efficiency of this conversion varies among individuals due to genetic differences in enzyme function, which may explain why some people experience stronger opioid-like effects from Kratom than others.

Why the Natural Formation of 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine Matters: Safety Considerations
The oxidation of Mitragynine into 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine plays a key role in Kratom’s effects. However, because this alkaloid remains a minor component in unprocessed Kratom, the plant’s effects are generally milder compared to synthetic opioids.
This is one reason Kratom has gained popularity as an alternative for pain management—it provides relief without the severe respiratory depression commonly associated with prescription opioids.
Understanding how this compound forms naturally helps consumers distinguish between safe, unaltered Kratom and potentially unsafe, artificially enhanced products.
To ensure safety and quality, users should purchase Kratom from reputable vendors that provide third-party lab testing to verify alkaloid content and confirm the absence of synthetic additives.
Ensuring Safe and Responsible Use
With 7-Hydroxy Mitragynine’s increasing popularity, ensuring product safety and responsible use is essential. Several key practices can help minimize risks:
- Buy from Trusted Vendors: Choose suppliers that offer third-party lab testing to verify alkaloid content and screen for contaminants like heavy metals and pesticides.
- Practice Moderation: Stick to moderate Kratom doses and avoid daily use to reduce the risk of tolerance and dependence. Taking occasional breaks can also help.
- Avoid Harmful Combinations: Never mix Kratom with other substances that affect the central nervous system, particularly alcohol, opioids, or benzodiazepines.

Conclusion: Understanding & Using 7-Hydroxy Safely
7-Hydroxy Mitragynine is one of Kratom’s most potent alkaloids, contributing to its analgesic and sedative properties despite being present in small amounts.
By understanding its natural formation, users can make informed choices and prioritize safety while benefiting from Kratom’s unique effects.